Whether you’re seeking a solar system or you already have one, you’ve probably considered a home solar battery system. But despite solar battery systems being quite popular these days, many homeowners don’t know very much about them. Therefore, let’s dive into the technology behind them. Then, uncover your available solar battery options.
Using household solar power provides some amazing benefits. For example, solar systems save you big money and they help the environment. In this article, discover another great benefit from home solar: adding a solar battery system provides you with energy independence.
Read more to learn about the technology behind solar battery systems and to check out your available solar battery options.
How a solar battery system works
Your solar panels produce the most electricity mid-day when your household uses the least amount of power. Therefore, use a solar battery system to store that extra electricity when it’s flowing in. Then, use that power when there’s little to no sunlight – power your home for free every night.
If tied to the grid with a hybrid solar system and a blackout occurs, solar battery systems keep homes powered. That means, your day will continue un-interrupted! Usually, your internet will remain live during a blackout. That’s because your internet is fed by a separate wire – it’s not related to your grid.
Most existing solar systems that use multi-mode inverters have energy storage capability. Hybrid solar inverters have battery connections and controls built right in. That makes adding a solar battery system much easier in the future.
Solar battery system types
In the marketplace, you’ll find many different solar battery system types. But of course, most residential systems use either lead-acid or lithium-ion solar battery systems. Lead-acid batteries are the type used in automobiles and have been around a long time. Lithium-ion batteries are like those use in smartphones.
As you’ll find, there are two main lithium-ion chemistries used for solar batteries. The first is NMC or Nickel Manganese Cobalt. The second is LFP or Lithium Iron Phosphate. NMC batteries, like the LG Chem Prime, have been around a bit longer, making them slightly less expensive.
Many homeowners choose to use lead-acid batteries instead of lithium-ion batteries. The main reason for this is that they cost less. But, there are downsides to them. First, they usually have a shorter lifespan. Next they contain a lower power capacity. Finally, they require regular maintenance.
Lead-acid solar battery system performance
Traditionally, lead-acid deep cycle battery systems were the most common and reliable option for off-grid solar systems. Though a proven technology lasting over a decade, keep them at room temperature and don’t discharge them often.
To explain why room temperature is so important, both high temperatures and low temperatures degrade them over time. Also, when you fully drain lead-acid batteries damages occur internally. In fact, fully draining a lead-acid battery can cause it to completely die and no longer take a charge.
Lithium-ion solar battery system bank options
The best battery option for your solar system is a lithium-ion battery bank. It’s an advanced storage device optimized for long life, fast recharge, and high efficiency. But most notably, lithium-ion battery banks are quite popular for their high efficiency that ranges from 92% to 98%.
Next, lithium-ion batteries are lightweight, compact and scalable. On top of that, they provide flexible sizing for additional capacity down the road. In other words, install additional lithium-ion batteries in the future as you’re power needs increase. Or, add them to increase power storage for peace of mind.
An amazing advantage to lithium-ion batteries is their ability to sustain a low or partial charge level for long periods. To explain, there are no negative effects to sustained low or partial charge levels. Also, lithium-ion batteries provide high charge rates – charge times are up to 70% faster than lead-acid.
Using EV batteries for solar battery systems
There’s a new and emerging technology known as V2H or Vehicle to Home. In fact, it’s slowly being introduced and implemented into many next-generation EV’s or Electric Vehicles. EV’s are essentially a large battery on wheels that can store excess solar energy.
Power your home and charge your EV using a specialized charging system called a smart EV charger. These are bi-directional, so they can deliver power to your home or receive solar power for charging. Smart EV chargers require an add-on meter to measure the energy flow to and from your home.
Calculate solar battery system size
Knowing that the sun doesn’t shine at night and during cloudy or stormy days, your solar battery system must carry you through. Standard solar system sizing calls for three days of autonomy. That means, when your solar panel array isn’t producing power, your solar battery system will only be down to 50% State-Of-Charge (SOC) after three days.
Generators are often used for power backup when using an off-grid solar system. As such, the standard sizing is the balance between your solar battery system and the frequency you need to use that generator. A generator is recommended to bridge long periods without sunlight, like winter time.
Generally, it’s better to have more battery capacity than you need in order to meet your household power requirements. The faster you discharge batteries, the faster the batteries will wear out. Therefore, your solar system battery bank should be sized larger than your household power demand requires.
Calculate the minimum battery capacity in AH or Amp Hours. First, take the watt-hours per day and multiply them by three days. This represents a 50% depth-of-discharge on your batteries. Then multiply by two and convert the kWh result into AH. Just divide by the battery bank voltage (12V, 24V or 48V).
Check out this informative article to learn exactly how to calculate what must go into your solar system:
OFF-GRID SOLAR CALCULATOR: How to calculate solar system size
Calculate household energy demand
Although your household energy demand varies throughout the year, start by calculating the basics in kWh. To begin, water usage, appliance usage, and general electricity usage is where to start. Keep in mind, only calculate water-usage if you use an electric water pump to provide water to your household.
If your household uses a water pump, check your water pump’s wattage – it will vary from 250W to 1,100W. Then, take the wattage of your water pump and multiply it by the number of daily hours it runs. Finally, divide that by 1000 for the number of kWh your pump uses.
Calculate each appliance individually. As such, use the wattage value for each of your own electrical appliances and products. This will provide the most accurate estimate. Then, add them all together to calculate your total annual energy consumption.
Estimate the number of daily hours each electric appliance and product runs at the most. For example, estimate the number of hours you use each electronic device. Examples include TVs, computers, gaming systems, home audio, and so on. Then, calculate each based on the wattage stated on each label.
Performing the household energy calculation
To determine your daily energy consumption, use the following formula:
(Watts × Daily hours used) ÷ 1000 = Daily kWh of consumption.
To calculate your annual energy consumption, use the following formula:
Daily kWh of consumption × Number of days used per year = Annual energy consumption.
This is a statement about annual electricity consumption in the U.S. by the U.S. Energy Information Administration:
“In 2020, the average annual electricity consumption for a U.S. residential utility customer was 10,715 kilowatthours (kWh), an average of about 893 kWh per month. Louisiana had the highest annual electricity consumption at 14,407 kWh per residential customer, and Hawaii had the lowest at 6,446 kWh per residential customer.”
Estimating home appliance power usage
In the following article from Energy.Gov about estimating appliance and home electronic power usage, estimate the total electricity used by your appliances with the following four methods:
- Review each Energy Guide label to estimate the individual unit’s average energy consumption.
- Use an Electric Consumption Meter to uncover how much electricity each appliance consumes.
- Install a whole-house energy monitoring system to monitor your actual energy usage.
- Calculate your total annual energy consumption using the formulas shown below.
Solar energy independence from off-grid solar
Starting with off-grid solar systems, over 300,000 homes use them for solar energy independence around the world. They know that when connected to the grid, they’re dependent on an external supplier, the utility company, for all their power. And when that power grid goes down, so does their power supply.
There’s a balance between your off-grid solar system size and your electrical needs. In order to provide true unbroken solar energy independence, your battery bank must be quite large. It must get you through long periods of little to no sunlight. Also, a backup generator may be needed depending on your region.
Solar energy independence from hybrid solar
When referring hybrid solar assets, you’re talking about a self-sustaining household electrical system that is also connected to your local electrical grid. That means, this system provides three sources of electricity: solar power, battery bank power, and power from your local electrical grid.
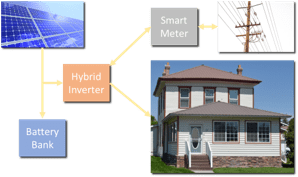
Many solar system variations and custom options exist. And, there’s an assortment of essentials to identify ahead of time. Then, you can design your solar system. Keep in mind, it’s important to understand the basic system and components before installation.
Keeping your connection to your power grid allows you to receive unlimited electricity. That means, if you use big equipment or appliances, your electrical system will support it without fault. And if the summer heat steeply rises, use air conditioning to your heart’s content and stay cool throughout the day.
Off-grid solar systems
Starting with off-grid solar systems, over 300,000 homes use them for solar energy independence around the world. They know that when connected to the grid, they’re dependent on an external supplier, the utility company, for all their power. And when that power grid goes down, so does their power supply.
There’s a balance between your off-grid solar system size and your electrical needs. In order to provide true unbroken solar energy independence, your battery bank must be quite large. It must get you through long periods of little to no sunlight. Also, a backup generator may be needed depending on your region.
Hybrid solar systems
When referring hybrid solar assets, you’re talking about a self-sustaining household electrical system that is also connected to your local electrical grid. That means, this system provides three sources of electricity: solar power, battery bank power, and power from your local electrical grid.

Many solar system variations and custom options exist. And, there’s an assortment of essentials to identify ahead of time. Then, you can design your solar system. Keep in mind, it’s important to understand the basic system and components before installation.
Keeping your connection to your power grid allows you to receive unlimited electricity. That means, if you use big equipment or appliances, your electrical system will support it without fault. And if the summer heat steeply rises, use air conditioning to your heart’s content and stay cool throughout the day.
Solar system installation
First, do not attempt to install your own solar system unless properly trained, experienced, and correctly certified to do so. In other words, this type of installation is not a DIY project. To explain, solar component installation and wiring requires an electrician and a construction contractor to do it right.
For a comparison, installing a complete solar system is like installing a circuit breaker unit along with other major electrical systems. One primary component of a solar system is the solar power inverter, which powers your entire home. That means, safety and reliability is no different between the two.
Construction skills are also necessary to install a solar system. To elaborate, solar panel arrays are typically secured on top of existing structures. As such, the physical connections must be strong and reliable. Sometimes, structures are built from the ground up to carry the load of your solar panel arrays sufficiently.
To learn how to find the best solar system installer near you, check out the following article:
SOLAR INSTALLERS NEAR ME: How to pick a solar installer to do it right



