How can an Electric Vehicle store solar energy, power your home, and sell excess electricity back to your power grid? Since an electric vehicle is essentially a large battery on wheels, it can store excess solar energy. Then, a bidirectional battery charging system can perform all three functions.
Electric Vehicles or EVs will help to power millions of homes in the near future. To explain, these homes simply harness the battery power of EVs. The ability to use these huge batteries connected through a bidirectional battery charging system fits future power management. And, they provide for cleaner grids – less burning of fossil fuels.
Now, continue reading to learn more about bidirectional battery charging systems and how they work.
Can your EV power your home with a bidirectional battery charging system?
As the world transitions from large power plants to a more distributed grid, the likelihood of power outages will increase. Also, the duration of those outages will increase as well. The traditional household solution is to purchase a portable or permanently installed generator to provide backup power.
But EVs present another opportunity for backup power. As such, these EVs all have batteries large enough to theoretically power a home for several days. The trick is transferring the electrical energy from an EV into useful home AC power. As mentioned, this is done using a bidirectional battery charging system.
A number of cars, including the VW EVs and the Nissan Leaf, will be available in 2022 and beyond. But so far, only Ford has announced the requisite components to make bi-directional charging work in a house. The system is called Intelligent Backup Power and it’s available in conjunction with the F-150 Lightning.
Ford has partnered with Sunrun, a major nationwide solar system installer to ease this installation process. Sunrun can add a solar cell array to the system to provide free solar electricity. This will stretch how long the system can power your house while maintaining the charge in your Lightning’s battery.
Vehicle-to-home or V2H to power your home
The biggest factor in using an EV to power your home is whether your vehicle has bidirectional charging. EVs with this capacity use electricity to charge their batteries. And, they send electricity from a charged battery to your household. But of course, the size of the vehicle’s battery determines its effectiveness.
There are two ways to judge how big your battery is. The first is the total amount of electric fuel stored in the battery. This is the most widely publicized number from EV manufacturers because it determines how far the car can drive.
Batteries in electric sedans like the Nissan Leaf or Tesla Model S may store 80 to 100 kilowatt-hours of electricity. For reference, 1 kilowatt-hour (kWh) is enough energy to power a typical refrigerator for five hours.
A typical U.S. household uses around 30 kWh per day, depending on its size and which appliances people use. That means, your EV can store enough electricity for the energy needs of a typical home for a couple days.
Vehicle-to-grid or V2G to help the grid
V2G involves using electricity from your EV to help stabilize your local grid. This is also done through a bidirectional battery charging system. It’s typically part of a VPP or Virtual Power Plant. Subject to defined parameters, your power provider controls when your battery is charged or discharged.
For example, your EV battery is charged when energy demand is low. And, it’s discharged when demand is high.
Offset the grid and earn money
Many EVs are being made with the ability to use their onboard battery to send power back to the grid. As such, they have a built-in bidirectional battery charging system. Whether used for household electricity or the grid, these technologies are led by governments and electric car manufacturers. The goal is to balance the demand on the grid.
A bidirectional battery charging system combined with solar net metering helps utility companies manage peak electrical loads in your neighborhood. This supplies smoother electrical-demand curves by reducing strain on power grids. As such, it prevents energy losses in long-distance electrical transmission and distribution lines.
To briefly explain energy loss, the longer the distance electricity travels, the more energy it looses. Therefore, supply electricity to your neighbors to greatly reduce that distance. In the end, solar net metering saves money for you and utility companies by reducing their electrical loss – win, win!
Electricity sent back to the grid also helps utility companies balance the cost of purchasing electricity from other resources. This is especially true during hot summer months when electricity is often the most expensive. Most homes will produce excess electricity during those summer months.
Smart meters and a bidirectional battery charging system
Net metering is the best way to go since it allows you to store the excess electricity you produce. As such, use that power at a later date. In fact, you’ll save tens of thousands of dollars over the lifetime of your solar system. This is done by offsetting your need for electricity using you EV and a a bidirectional battery charging system.
Be sure to check out the DSIRE or Database of State Incentives for Renewables and Efficiency to learn more. The DSIRE tracks net metering and provides other policies.
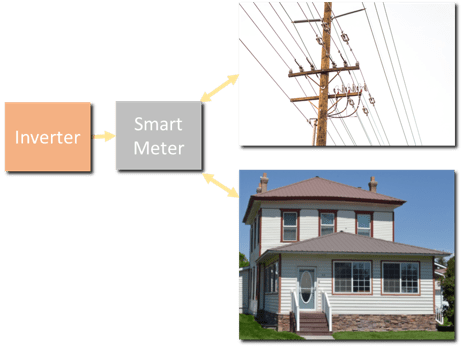
As a replacement to your standard meter, a smart meter provides you with something called net metering. To explain, net metering analyzes and displays your local power grid’s electrical exports and imports.
Smart meters manage additional factors too. To explain, they handle both the power generated by your solar system and your household power consumed. When exporting electricity, your meter spins backward. As a result, your electric bill receives applied credits each month.
Earn money with your EV and a bidirectional battery charging system
This is where the rubber meets the road regarding solar and an EV connected to a bidirectional battery charging system. The question “How much does solar power save on electricity bills?” is asked by everyone and for good reason. We want to generate our own power instead of paying a utility company to generate power for us. That saves money by design.
As you’ve seen on your electricity bills, prices go up every year. Compare that to monthly payments on your solar system loan. Obviously, loan payments do not go up and they eventually come to an end once paid in full. That means, you will no longer have an electric bill if your solar system is fully sufficient.
The amount you save on your electricity bills by using solar power is directly proportional to the sufficiency of your solar system. To explain, if the your solar system is big enough to provide for all your electricity needs, your electric bill will drop to zero. On top of that, some solar systems let you sell back your excess power.
In the next section, let’s take a look at hybrid solar systems. They can be completely self sustaining and they allow you to sell back excess electricity. In other words, they allow your home to become a power “source” for your local utility company. How cool is that?
Watch this short video detailing the answer to “how much does solar power save on electricity bills?”
In the following video, Eric Martineau, the founder and owner of Just Get Solar, reveals detailed insight showing exactly how much using solar power saves you on your electricity bills. First, he quickly reveals the top 10 reasons people choose solar. Then, he focuses on how to save your hard-earned money.
Hybrid solar systems sell back excess electricity
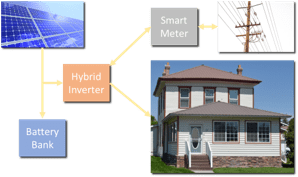
Introducing hybrid solar, a self-sustaining household solar system that also connects to the power grid. That means, hybrid solar systems provide power from three sources: solar energy, battery bank backup power, and electrical utility grid power.
With a hybrid solar system, the components work together to power your household without interruption. To explain, your solar panel array provides power by converting sunlight into free electricity. Then, your battery bank stores excess electricity for nighttime use. Finally, your local power grid connection provides extra power when needed it and allows you to sell excess electricity back to them.
The center of your hybrid solar system is a multi-mode inverter, which performs two primary functions. First, it converts DC or direct current from your solar panel array and battery bank to 120V AC or Alternating Current to your household. Then, it charges and manages your battery bank charge levels, which prolongs battery life quite well.
Hybrid solar inverters are also able to export or sell excess electricity back to your utility company. As mentioned before, your hybrid solar system becomes a “source” of power providing you with credits on your bill.



